Leading Handmade Rug Manufacturer
Serving Retailers, Designers and Wholesalers in the USA
WEAVING TECHNIQUES
Unveiling the Rich Tapestry
of Himalayan Rug-Manufacturing Traditions
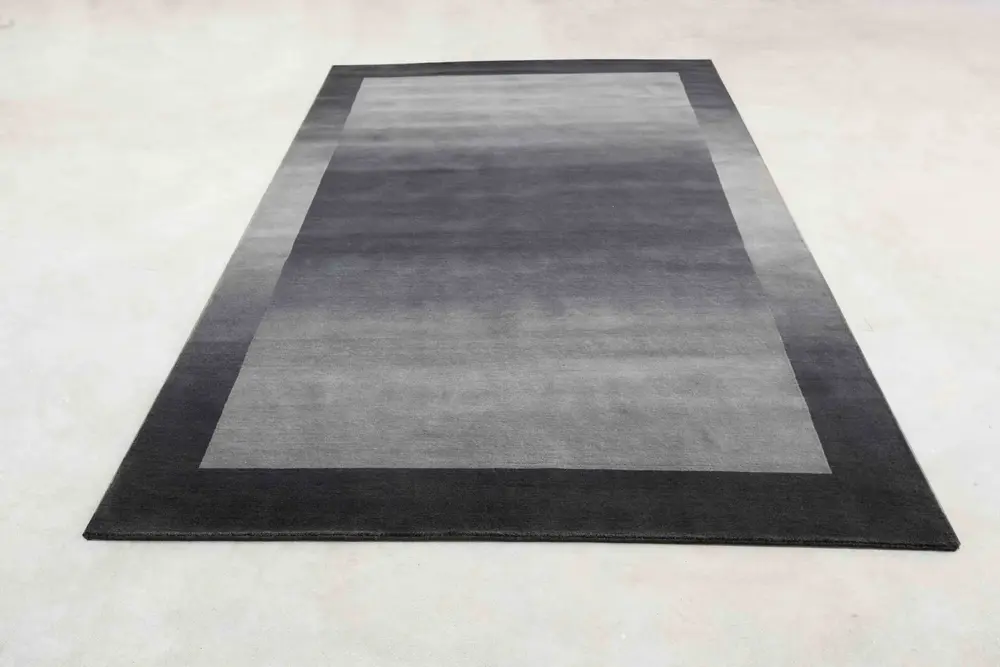
From Nepal’s diverse landscapes come natural treasures: resilient wool, shimmering silk, and rare fibers like nettle, hemp, and bamboo. Beyond the nomadic regions, skilled artisans carefully source and handcraft these materials, creating rugs that resonate with American homes through quality, heritage, and timeless appeal.
We transform your space with
our Timeless Rugs
Partner With NP Rugs
Collaborate with Nepal’s leading rug manufacturer.
Partner With Us to Craft Premium Rugs for Global Interiors
Custom-Designed Rugs for Hotels, Boutiques & Interior Projects
Bulk Orders, Custom Sizes & Design Support for Trade Buyers
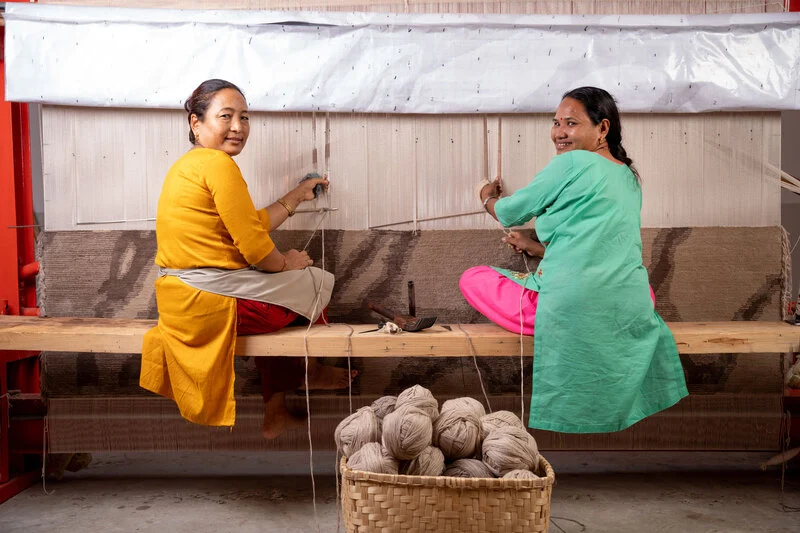
Preserving Heritage, Empowering Lives,
Our Artisan Village in Nepal
NP Rugs is engaged in a collaborative effort with UKAID Programs, working in
conjunction with Label STEP to develop and support artisan villages.
NP Rugs Wholesale & Trade Supply Program
NP Rugs is a dedicated handmade rug manufacturer supplying bulk quantities directly from Nepal. Our wholesale program is built for retailers, distributors, and interior project managers who need consistent quality, customizable designs, and factory-level pricing. We handle every stage, from sampling to production and export, ensuring dependable lead times and seamless logistics for our US partners.
BLOGS
Recent insights
Learn recent news and insights about the rug industry, logistics, and get updated about the trends