Nepal’s rug industry has long been a significant economic driver, known for its hand-knotted woolen carpets that have gained international recognition. However, in recent years, it has faced a 65% decline in exports due to various structural challenges. This report presents key data and trends shaping the Nepalese rug industry today.
Market Overview & Growth Trends
Key Statistics:
| Peak Export (1993/94): 3.33 million sq. meters | |
| Current Export (2025 Estimate): 600,000 – 700,000 sq. meters (⬇ 65%) | |
| Annual Revenue: Rs. 600 crore from rug exports | |
| International Share: 90% of Nepalese rugs are exported | |
| Production Units: 600+ small-scale carpet manufacturer |
Key Observations:
✔️ Initial boom due to lower costs, exclusive designs, and GSP tax exemptions
✔️ 1990s market saturation & competition from India and China led to decline
✔️ Rising demand for organic, natural-dye, and sustainable carpets in niche markets
Source: Nepal’s Carpet Globalization (2003) [PDF]; Industrialization Strategy for Nepalese Carpet Industry (2025) [PDF]
Key Export Markets & Revenue Data
Top Importing Countries & Export Figures (2025):
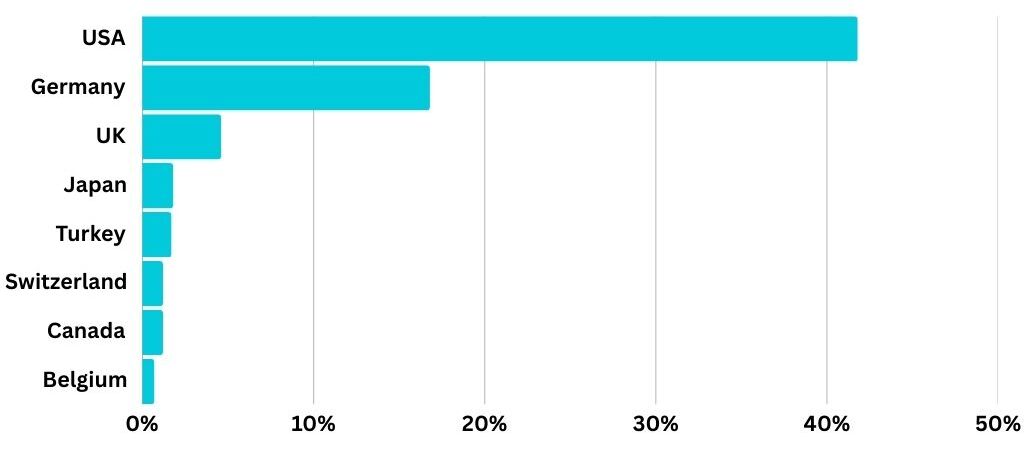
Source: Industrialization Strategy for Nepalese Carpet Industry (2025) [PDF]
Export Logistics & Supply Chain:
Air Freight (75% of exports) – via Tribhuvan International Airport
Land Route – Birgunj to Kolkata port for global shipment
Trade Preferences: Nepal benefits from GSP tax exemptions in major markets
Source: Hand Knotted Woolen Carpets Manufacturing [PDF]
Production Process & Labor Force
Workforce & Employment:

Source: Hand Knotted Woolen Carpets Manufacturing [PDF]
Materials & Methods:
- Traditional hand-knotted wool rugs dominate the industry
- New materials gaining traction: Hemp, Allo, Jute
- Shift to natural dyeing techniques as synthetic dyes fall out of favor
Challenges & Opportunities
Structural Challenges (Backed by Reports):
Export Decline: From 3.33M sqm (1993) → 0.7M sqm (2025) due to high global competition
Raw Material Dependency: 80% of wool is imported, making production costlier than India/China
Labor Costs vs. Productivity: Nepalese rugs cost 30-40% more to produce than Indian counterparts
Compliance & Regulations: Increased certification requirements (RugMark, Fair Trade) adding costs
Quality Issues: Lack of dye standardization leading to rejections in EU markets
High-Impact Growth Areas:
Eco-Friendly Carpet Boom: Demand for organic & naturally dyed rugs growing in EU/US markets
Handmade Certification Advantage: Nepalese rugs now qualify for “Handmade Label” in Europe
Luxury Market Positioning: Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands charging premium rates
Export Diversification: Focus shifting towards Turkey, UAE & Japan to reduce EU dependency
Government SEZs (2025-2030): Plans to establish dedicated carpet production zones
Future Projections (2025-2030)
Projected Export Growth: 10-15% annually if local wool production increases
Sustainable Material Shift: 35% of rugs expected to be eco-certified by 2030
Automation in Weaving: Introduction of semi-mechanical knotting to enhance productivity
Rural Relocation Strategy: Expected 20% cost reduction by shifting production outside Kathmandu
Conclusion & Policy Recommendations

To revitalize Nepal’s rug industry, immediate policy interventions are required:
- Subsidized Wool Farming: Cutting import reliance (80%) can reduce costs drastically
- Dye Standardization Program: Ensuring uniform quality for exports, reducing EU rejections
- Luxury Market Penetration: Positioning Nepalese carpets as handmade luxury via branding
- Infrastructure Boost: SEZs to reduce production & compliance costs
Infographic Summary:
🟢 Exports down from 3.3M sqm (1993) → 0.7M sqm (2025)
🟢 100,000+ artisans, 300,000+ indirect jobs
🟢 80% wool imported → Major cost driver
🟢 EU/US luxury segment prefers “Handmade Label”
🟢 SEZs & local wool can cut costs by 20%
🟢 Projected 10-15% growth with reforms
📌 Strategic focus: Local production, niche branding & cost efficiency!

